Ansys Enhances Mission Modeling with Cesium
To visualize complex multidomain scenarios—from urban environments to deep space—Ansys integrates Cesium with Ansys Systems Tool Kit (STK), Ansys Digital Mission Engineering (DME) Component Libraries, and Ansys RF Channel Modeler.
Both Ansys and Cesium have served the United States’ and allies’ aerospace and defense industries for decades, modeling multidomain systems of systems in time-dynamic environments. These simulations enable engineers to build and test virtually rather than experimenting on multiple physical prototypes, decreasing manufacturing costs and risk.
CesiumJS began at aerospace software company Analytical Graphics, Inc. and spun out as an independent company in 2019. Analytical Graphics, Inc. was then acquired by Ansys, which continues to leverage Cesium technology as Ansys Government Initiatives.
“Cesium has truly revolutionized the geospatial ecosystem, and driving for modern open standards is phenomenal,” said Shashank Narayan, CTO of Ansys Government Initiatives.
Simulations enable engineers to build and test virtually rather than experimenting on multiple physical prototypes, decreasing manufacturing costs and risk. Courtesy Ansys.
Ansys Systems Tool Kit (STK)
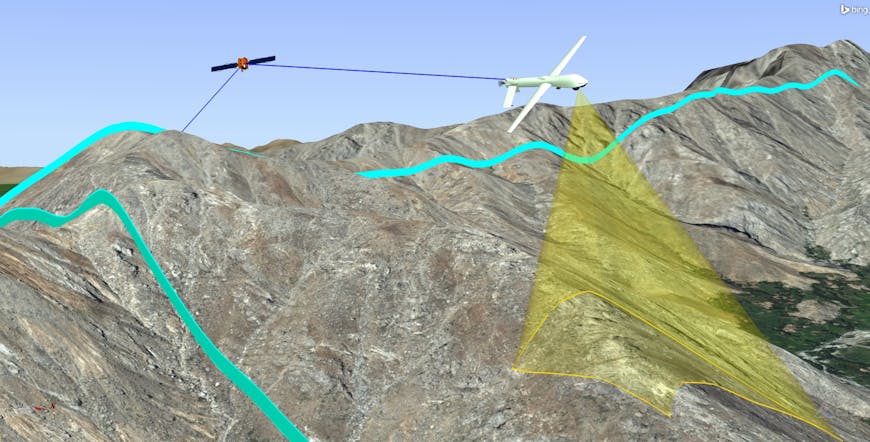
Released in 1989, STK is a physics-based mission modeling environment that incorporates visualization of land, sea, air, and space scenarios and the airplanes, spacecraft, and other vehicles and facilities that go with them. Users can model the relationships among the moving objects and apply constraints, such as clouds, terrain, and buildings, to assess their impact. For example, how might clouds affect imagery collection or navigation? How might flying in a canyon affect radio or internet access? For context and constraints, engineers can use STK's Geospatial Content Server (GCS) capability and integrate the CesiumJS globe and Cesium ion’s tiling pipelines. If STK users have Cesium ion accounts, they can seamlessly access Cesium World Terrain and Bing Maps Aerial imagery and include their own datasets, which can be tiled into 3D Tiles for optimal streaming and visualization.

Ansys and Cesium have served the United States’ and allies’ aerospace and defense industries for decades, modeling multidomain systems of systems in time-dynamic environments. Courtesy Ansys.
DME Component Libraries
DME Component Libraries are a collection of class libraries in .net and Java, which enable satellite propagation including maneuver modeling, aircraft flight modes, ground system routing, RF communication, and radar systems analysis. These libraries are ready to be deployed in a SaaS or individual workstation deployment. Engineers can use DME Component Libraries to build custom applications that incorporate analytical capabilities found in STK. DME Component Libraries increase precision and interoperability with Cesium ion SDK, which extends the open-source CesiumJS JavaScript library with additional 3D analysis tools and UI widgets.
.jpg?auto=compress%2Cformat&w=870)
DME Component Libraries increase precision and interoperability with Cesium ion SDK. Courtesy Ansys.
RF Channel Modeler
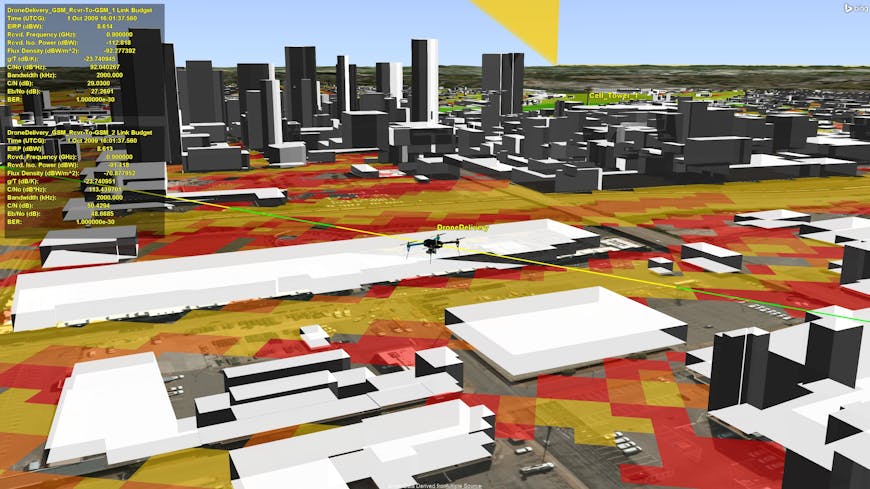
RF Channel Modeler addresses the needs of RF systems designers, telecommunications planners, and network engineers. It enables users to predict signal coverage, evaluate waveform performance in bespoke locations, mitigate interference, and achieve the right balance between coverage and capacity. High-fidelity modeling and simulation enables these users to better understand the growing complexities and sophistication of today’s communications systems while optimizing their proposed designs. RF Channel Modeler builds on top of STK and connects its dynamic mission modeling capabilities with high-fidelity datasets and ray tracing technologies to analyze system performance at individual channel levels. This solution relies on 3D Tiles to introduce the necessary high-resolution urban environment models, which can be streamed directly via Cesium ion for accurate city features and metadata. RF Channel Modeler’s workflow lets users add base stations, cars, airplanes, or other objects that may be needed to accurately analyze and assess the performance of modeled RF systems in its simulated environment.
Ansys RF Channel Modeler users can predict signal coverage, evaluate waveform performance in bespoke locations, mitigate interference, and achieve the right balance between coverage and capacity. High-resolution urban environment models can be streamed via Cesium ion for accurate city features and metadata. Courtesy Ansys.
With Cesium’s accurate, time-dynamic 3D globe and curated geospatial data, Ansys customers see their mission scenarios and perform analyses in real-world contexts.
Contact Ansys to learn more about their digital mission engineering solutions or connect with their team in the Cesium booth at I/ITSEC 2023, #559.
Note: We updated the DME Component Libraries segment of this story on May 31, 2024.