Cesium: Foundations
The Cesium: Foundations learning path will help you understand the basic concepts and terminology needed to progress through other Cesium learning paths.

Introduction
In this lesson, we will cover the Cesium platform and provide an overview of each component.
What is Cesium?
CesiumJS was created in 2011 by an Analytical Graphics Inc. (AGI) team for global-scale aerospace visualizations, and Cesium spun out as its own company in 2019. CesiumJS was offered as a free open-source software alongside Cesium ion as a commercial option to extend into a complete 3D geospatial platform.
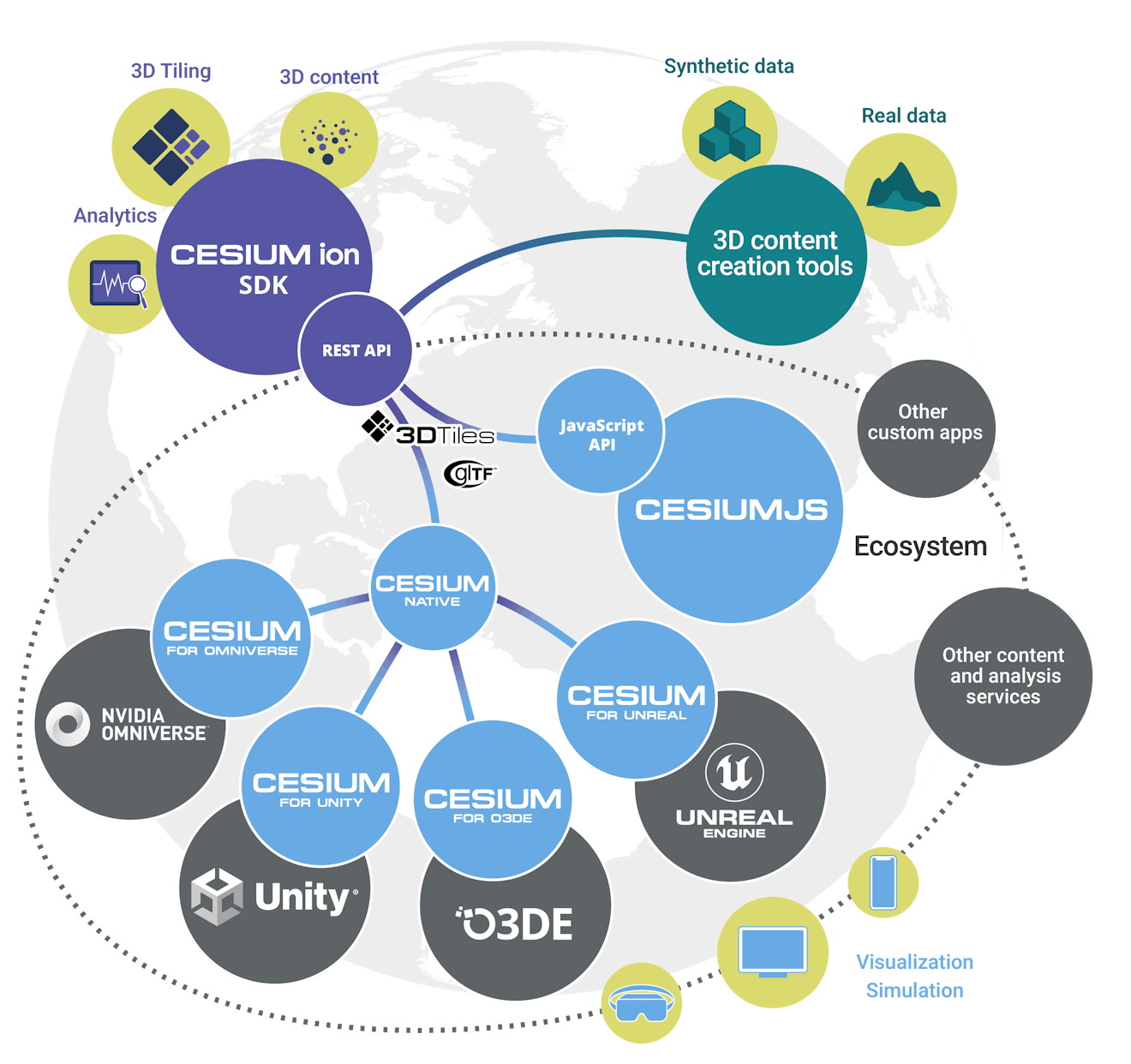
Cesium has also been central to creating an open ecosystem for 3D geospatial applications. Cesium was the original creator of 3D Tiles in 2015 and shepherded its acceptance as an Open Geospatial Consortium (OGC) community standard in 2019, now widely adopted by developers.
Cesium believes that openness and interoperability are the essential elements that will propel the entire 3D geospatial ecosystem forward. Today, Cesium operates across multiple runtimes, including CesiumJS, Cesium for Unreal, Cesium for Unity, Cesium for Omniverse, and Cesium for O3DE.
Assignments
- Read The Cesium Business Model to understand how Cesium balances open source and commercial software.
- Explore Cesium’s contributions to an open 3D geospatial ecosystem.
Additional resources
This section contains helpful links related to the lesson’s content.
- Browse the Building the Open Metaverse podcast co-hosted by Cesium’s CEO, Patrick Cozzi, and Marc Petit. Many episodes explore the relationship between 3D geospatial applications and an open ecosystem for developers.

Introduction
In this lesson, we will cover some of the core concepts in the 3D Tiles specification and discuss why 3D Tiles is essential within the Cesium platform.
What is 3D Tiles?
First, let’s cover a little history of 3D Tiles.
Soon after its inception in 2011, Cesium faced the problem of streaming large collections of 3D models from different sources, e.g., point clouds, photogrammetry, 3D buildings, vector data, etc. Unfortunately, the existing available approaches made streaming these datasets impractical, so Cesium set out to create a better alternative.
By 2015, Cesium had created the 3D Tiles specification for streaming massive heterogeneous 3D geospatial datasets. By 2019, the Open Geospatial Consortium (OGC) adopted the 3D Tiles specification as a community standard.
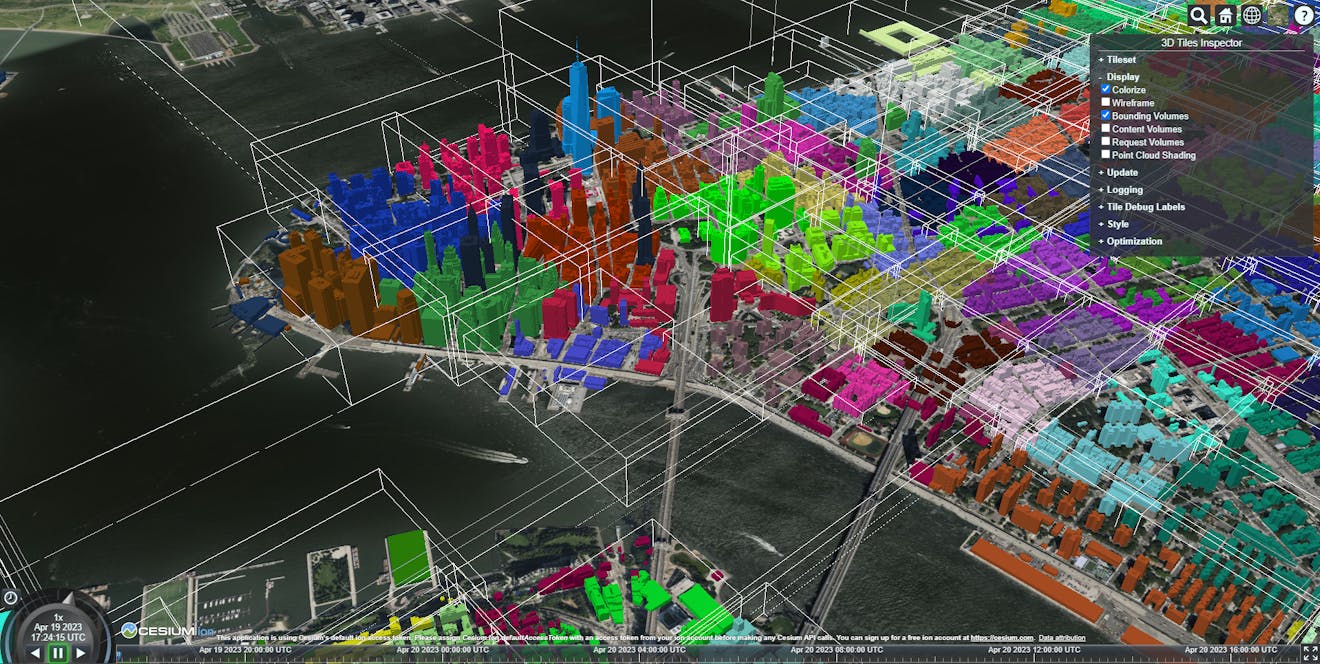
Bounding volumes for 3D Tiles. Each tile is one WebGL draw call.
What does the 3D Tiles specification achieve?
3D Tiles allow users to stream massive 3D datasets by limiting which portions of the dataset are loaded based on a Hierarchical Level of Detail (HLOD). Because the primary focus of 3D Tiles is streaming performance, their design enables them to compress and render their contents efficiently.
Assignments
- Take a few minutes to read Patrick Cozzi’s Introducing 3D Tiles blog post that describes the benefits of 3D Tiles and how they have enabled 3D geospatial applications worldwide.
- Read about how 3D Tiles Next, which the OGC adopted as 3D Tiles v1.1 in May 2023, expands on the existing specification
Additional resources
This section contains helpful links related to the lesson’s content.
- A 2022 VentureBeat article helps draw the connection between 3D Tiles and the metaverse.
- Detailed reference cards for 3D Tiles and 3D Tiles 1.1 include visuals for anyone unfamiliar with the underlying 3D or geospatial concepts.
- The OGC’s 3D Tiles specification provides the technical details of 3D Tiles.
Knowledge check
This section contains questions to check your understanding of this lesson. Review the content again if you’re having a problem answering a question.
- Why was the 3D Tiles specification first created?
- What are the ten core features of 3D Tiles?
- Why is metadata such a critical feature in the 3D Tiles 1.1 specification?

Introduction
In this lesson, we will look at Cesium ion and understand how it creates streamable 3D content.
What is Cesium ion?
Cesium ion began as the commercial extension of the free open-source software CesiumJS to create the most efficient pipeline for 3D Tiles.
Because we built ion as an end-to-end 3D platform, developers can upload their 3D content and host 3D Tiles in the cloud so that any visualization engine can stream the content. It is also free for non-commercial and non-government users, up to 5 GB of stored data, and users can secure their data through token-based access controls.

Cesium ion tiles, optimizes, and hosts 3D data.
Cesium ion also includes access to a curated set of 3D content that includes Cesium World Terrain, Cesium OSM Buildings, and Bing Maps imagery, all optimized for streaming. In addition, users can bring their data and combine it with the existing datasets that come with Cesium ion.
How can Cesium ion be used?
We built Cesium ion with openness and flexibility in mind. As a result of that approach, Cesium ion allows you to upload data from several utilities that create 3D content. See this list.
Cesium ion’s REST API allows you to leverage ion’s tiling and streaming capabilities from existing applications. In addition, many clients and engines have built-in support for streaming from Cesium ion; see this list.
Assignments
- Review the Tiler Data Types and Formats page. Each data type listed above also has a tutorial you can access on the same page.
- Browse the Cesium ion integrations page to see if your preferred software is listed. If it isn’t listed, look at the community forum to see if it is in an upcoming release.
Additional resources
This section contains helpful links related to the lesson’s content.
- If you’re interested in Cesium ion’s launch, read the first blog post about the platform.
- You can read an overview to learn how Cesium designed the original server architecture for ion.
- Cesium ion’s REST API tutorial provides instructions on how to set up and utilize the potential of ion with your existing applications and workflows.
- You can dive into the reference documentation to learn about ion’s REST API.
Knowledge check
This section contains questions to check your understanding of this lesson. Review the content again if you’re having a problem answering a question.
- What 3D content does Cesium include with Cesium ion?
- What types of data does Cesium ion support?
- What clients and engines have built-in support for streaming from Cesium ion?
- How can you integrate existing applications or workflows with Cesium ion?
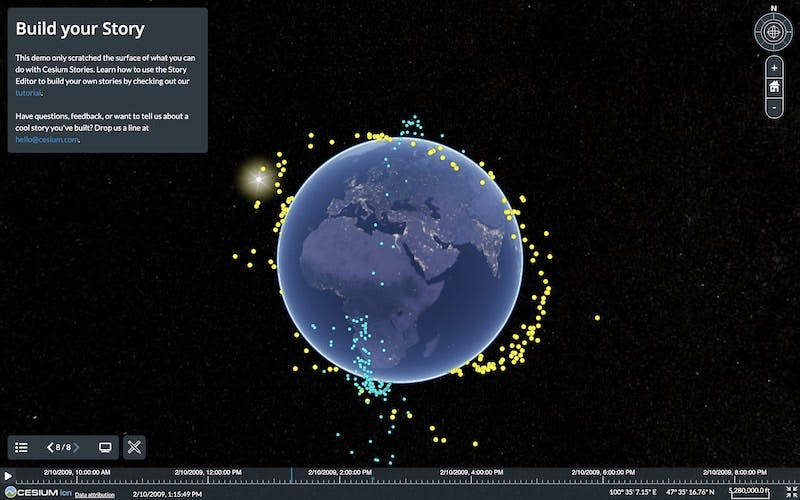
Cesium Stories allow anyone to create presentations with their 3D geospatial data.
Introduction
In this lesson, we will look at Cesium Stories to understand how you can use them to create 3D geospatial presentations.
What is Cesium Stories?
Cesium Stories is a cloud-based app available to anyone with a Cesium ion account for creating presentations using their own 3D geospatial data, which they can share on the web without writing a single line of code.
Users can create Cesium Stories with 3D data, including imagery, models, terrain, and point clouds. These are processed into 3D Tiles, allowing anyone to easily share or stream their presentation through a mobile or desktop browser.
To help explain Cesium Stories, we have a Cesium Story to demonstrate how powerful the app can be.
Click through the slides to see how powerful Cesium Stories can be.
Assignments
- Create an interactive 3D presentation with Cesium Stories.
- Complete the Visualizing Time Dynamic Data with Cesium Stories tutorial.
- Practice styling 3D Tiles in Cesium Stories.
- Using the skills you honed in this lesson, create your unique Cesium Story using your 3D data or open datasets like the City of Melbourne’s.
Additional resources
This section contains helpful links related to the lesson’s content.
- If you're looking for inspiration on using Cesium Stories, see how Professor Hidenori Watanave uses Cesium Stories to capture the extent of damage in Ukraine.
- This blog post shows another example of using Cesium Stories to share insights.
Knowledge check
This section contains questions to check your understanding of this lesson. Review the content again if you’re having a problem answering a question.
- Which programming language do you need to know to use Cesium Stories?
- How can you share your Cesium Story with others?
- How can you control the playback speed of time-dynamic data?
- Which type of metadata is needed to use the styling tool in Cesium Stories?
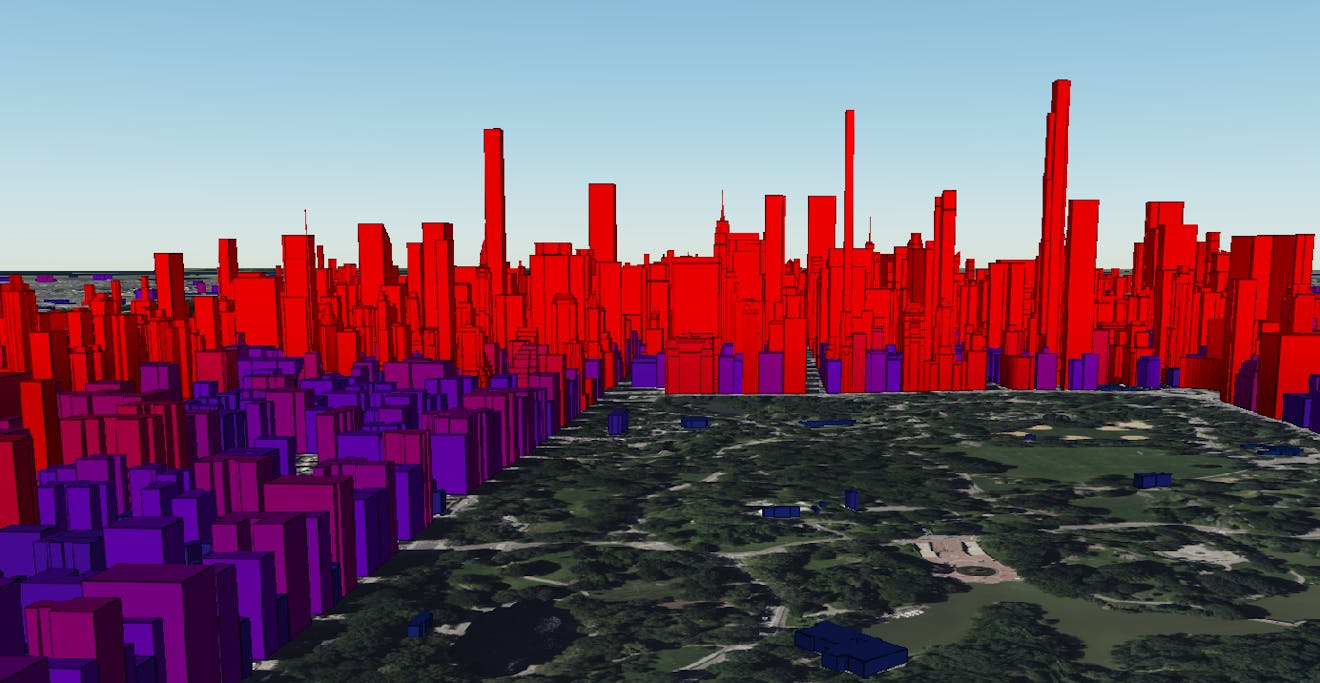
Now that you understand the foundational concepts of Cesium, put them into practice. Before progressing to the next course, create a Cesium Story that includes the following concepts:
- Multiple data formats (3D models, point clouds, imagery, etc.)
- Time-dynamic data
- Styling and filtering
- Tell a story with your data
We would love to see what you create, so feel free to share your Cesium Story with the Cesium community or share and tag us on LinkedIn or Twitter.
Consider starting CesiumJS: Fundamentals and working your way to becoming a Cesium Certified Developer.